Mpox Outbreaks Continue in Late 2023
The World Health Organization (WHO) today reported that the multi-country mpox outbreak continues at a low transmission level in the European Region and the Americas.
The 30th WHO Situation Report, published on November 25, 2023, offers insights regarding the latest epidemiology and a particular focus on the ongoing and evolving epidemiology of mpox in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC).
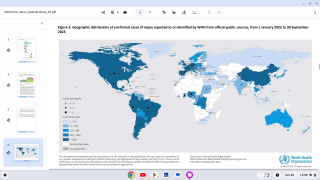
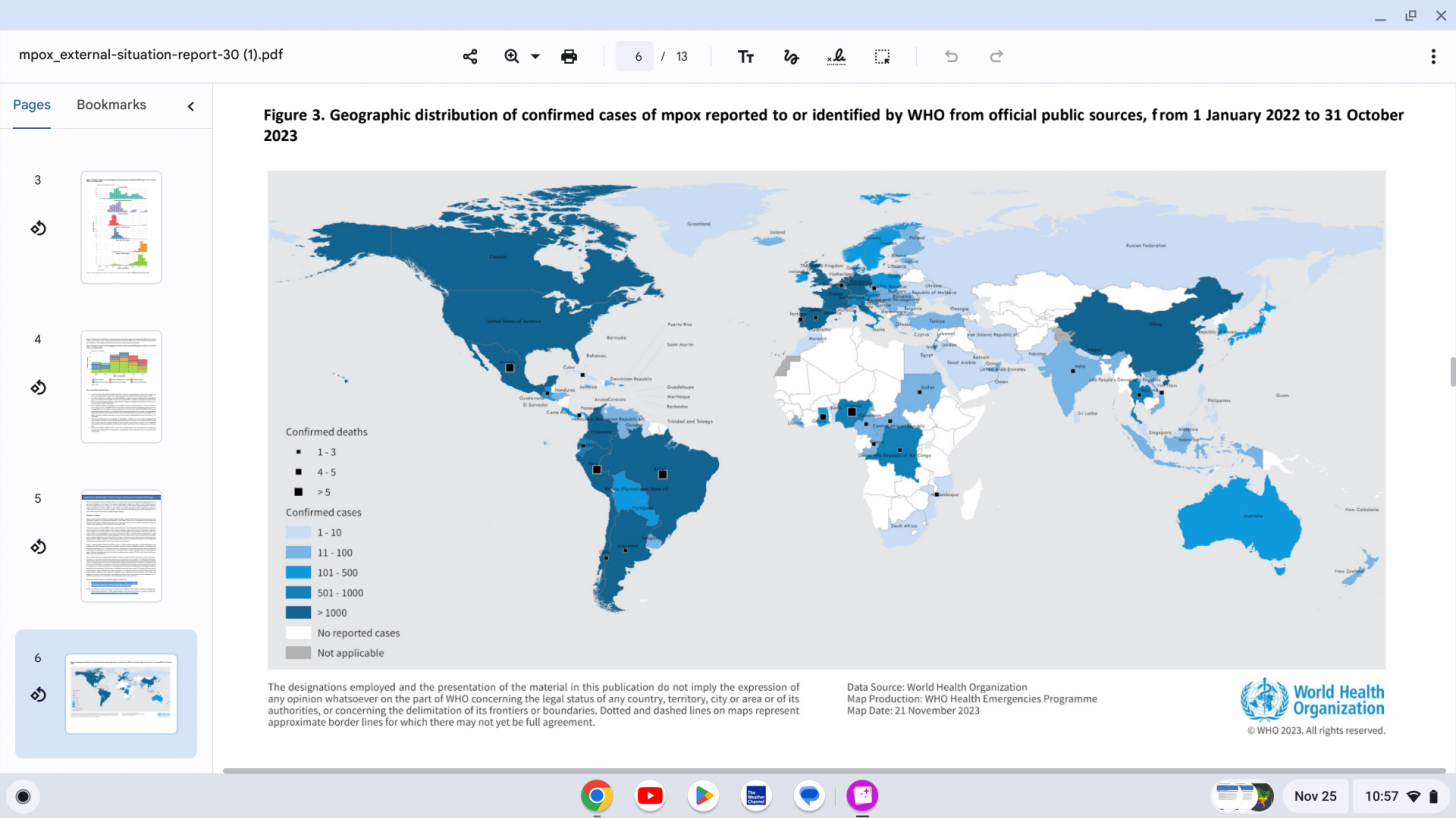
The WHO confirmed that from January 2022 through October 31, 2023, a cumulative total of 91,788 laboratory-confirmed cases of mpox, including 167 deaths, have been reported from 116 countries/territories/areas.
The countries that have reported the highest cumulative number of mpox cases are the United States (30,771), Brazil (10,967), and Spain (7,647).
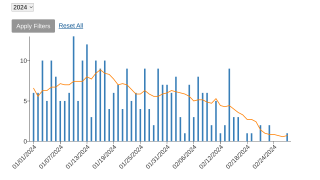
In October 2023, a 23% decline in new cases (668) was reported during the previous month.
Most cases last month were reported from the Western Pacific Region (30%) and the European Region (25%). Germany reported the highest relative increase in cases (n = 49 vs. n = 14) in the European Region.
In Africa, the DRC recently confirmed a total of 12,569 suspected mpox cases, including 581 suspected deaths (case fatality ratio: 4.6%).
This is the highest number of annual cases ever reported by the DRC, with new cases in geographic areas that had previously not reported mpox, including Kinshasa, Lualaba, and South Kivu.
Furthermore, a cluster of mpox cases documented the sexual transmission of MPXV Clade I among men who have sex with men.
The WHO says mpox is an infectious zoonotic disease caused by monkeypox virus (MPXV). Human-to-human transmission of mpox through close contact has been reported since the 1970s.
However, the natural reservoir of the MPXV remains unknown.
From a prevention perspective, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Advisory Committee for Immunization Practices unanimously recommended broader and more routine use of the mpox vaccine to prevent the disease in people at risk for mpox.
The CDC Director adopted the Committee’s recommendation in October 2023, and it is now official. This interim recommendation will be revisited in 2-3 years.
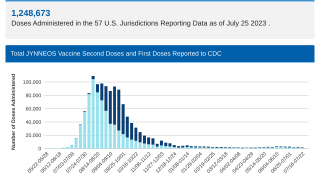
The CDC now recommends vaccination with the two-dose JYNNEOS® (MVA-BN®, IMVAMUNE®) vaccine series for adults at risk for mpox.
JYNNEOS is based on a live, attenuated vaccinia virus, Modified Vaccinia Ankara, which is incapable of replicating in the human body yet can elicit a potent immune response.
On September 8, 2023, the CDC confirmed that JYNNEOS is not 100% effective.
The CDC reported in October 2023 JYNNEOS Vaccine Effectiveness against mpox ranges from 36% to 75% for 1-dose vaccination and 66% to 89% for 2-dose vaccination.
Our Trust Standards: Medical Advisory Committee