Severe Malaria Treatment Approved For the USA

The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced the approval of Artesunate for injection to treat severe malaria in adult and pediatric patients.
This is important news since there had been no FDA-approved drug for the treatment of severe malaria in the USA since the marketing of quinidine was discontinued by the manufacturer in March 2019.
The FDA said on May 26, 2020, the treatment of severe malaria with intravenous (IV) Artesunate, 110 mg, powder and solvent for the solution, should always be followed by a complete treatment course of an appropriate oral antimalarial regimen.
“This approval will now give patients more access to a lifesaving drug,” said John Farley, M.D., acting director of the Office of Infectious Diseases in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
“Furthermore, the risk of developing severe malaria emphasizes the importance of taking medications to prevent malaria and using mosquito avoidance measures when traveling to malaria-endemic areas.”
Prior to this FDA approval, IV Artesunate was only available to patients through the Expanded Access Program, which allowed the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to provide IV artesunate to U.S. patients with severe malaria and to patients with uncomplicated malaria, who are unable to take oral medications under an investigational new drug (IND) protocol.
Amivas LLC said it ‘will now manufacture, distribute, and commercialize Artesunate for Injection and is completing the set-up of a nationwide product distribution network.’
The development of Artesunate for Injection in the US has been under US Army Medical Research and Development Command (USAMRDC). Within USAMRDC, the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research and the US Army Medical Materiel Development Activity joint collaborative work has provided the CDC a constant supply of IV artesunate since 2007.
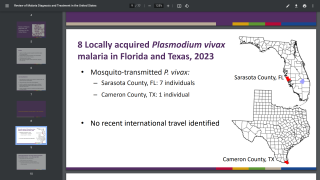
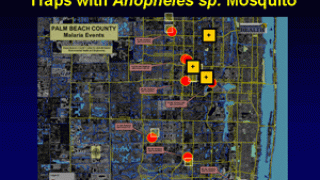
According to the CDC, approximately 2,000 cases of malaria are diagnosed in the United States each year, with 300 of those infected having severe disease. Most people diagnosed with malaria in the United States acquire it during travel to countries with malaria.
Malaria is a parasitic disease transmitted by a mosquito bite.
People with malaria often experience fever, chills, and flu-like illnesses, and without appropriate treatment, they may develop severe complications, such as kidney failure, seizures, mental confusion, coma, and death, says the CDC.
The safety and efficacy of IV artesunate for the treatment of severe malaria were primarily evaluated in a randomized controlled trial in Asia (Trial 1) and a supportive published randomized controlled trial in Africa (Trial 2).
Trial 1 enrolled 1,461 patients who received either IV artesunate or the comparator drug quinine and included 202 pediatric patients younger than 15 years.
Trial 2 included 5,425 randomized pediatric patients younger than 15 years of age with severe malaria who were treated with artesunate or quinine.
In both clinical trials, the number of patients treated with artesunate who died in the hospital was significantly lower than the number who died in the control group treated with quinine.
In Trial 1, the most common adverse reactions in patients with malaria treated with IV artesunate were acute renal failure requiring dialysis, hemoglobinuria, and jaundice.
The safety profile in Trial 2 was generally similar to Trial 1.
Artesunate should not be used in patients with a known serious allergy to Artesunate, such as anaphylaxis.
Amivas is a US joint venture focused on the development, manufacture, and commercialization of therapeutic products for the treatment of infectious diseases. Headquartered in Frederick, Maryland, Amivas was formed in 2016 expressly for the purpose of bringing treatments to market for rare and neglected tropical diseases.
The FDA granted this application Priority Review designation, under which the FDA’s goal is to take action on an application within an expedited time frame and Orphan Drug designation, which provides incentives to assist and encourage the development of drugs for rare diseases.
The FDA is an agency within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, protects the public health by assuring the safety, effectiveness, and security of human and veterinary drugs, vaccines and other biological products for human use, and medical devices.
Precision Vaccinations publishes FDA approved treatment news.
Our Trust Standards: Medical Advisory Committee