For Certain Children, 2 Flu Shots Confer Better Protection

Young children, especially those younger than 2 years of age, are at an increased risk of hospitalization and complications from annual influenza viruses.
And, a new study published in JAMA on May 4, 2020, finds a double-dose of the flu vaccine was more effective than a single dose, in supporting influenza vaccine-naive children.
In this case-control study including 7533 children, vaccine-naive children aged 2 years or younger, who received 2 doses of influenza vaccine in their first vaccination season were less likely to test positive for influenza than those who received 1 dose.
This study’s results suggest that the burden of influenza among young children in the USA might be reduced by improving adherence to an initial 2-dose series of influenza vaccination in previously unvaccinated children.
Specifically, this study of 7,533 children, a total of 3,912 children (52%) were unvaccinated in the enrollment season, 2,924 children (39%) were fully vaccinated, and 697 children (9%) were partially vaccinated.
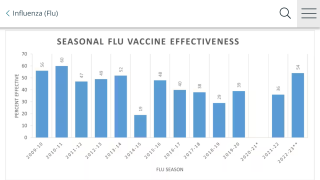
And the adjusted vaccine effectiveness (VE) against any influenza was 51% among fully vaccinated children and 41% among partially vaccinated children.
Among 1,519 vaccine-naive children aged 6 months to 2 years, the VE of 2 doses in the enrollment season was 53%, while the VE of 1 dose was just 23%.
These new findings reinforce prior flu shot studies that have consistently shown children who were completely vaccinated were "more likely to achieve a protective level of antibody titers and less likely to have an office visit for influenza-like illness," noted physicians in an accompanying editorial in JAMA.
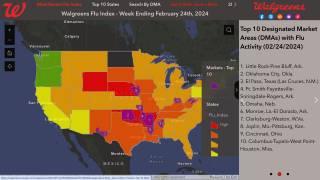
As of April 25th, there have been 170 pediatric fatalities reported during the 2019-2020 flu season in the USA.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommends that children between age 6 months and 8 years who have never been vaccinated, or who received only a single flu vaccine dose in previous seasons, receive 2-doses, administered at least 4 weeks apart.
These CDC recommendations apply to U.S.-licensed influenza vaccines used within Food and Drug Administration-licensed indications. Updates and other information are available from the CDC's influenza website.
The CDC suggests influenza patients and healthcare providers should check this site periodically for additional information.
Precision Vaccinations publishes influenza vaccine news.
Our Trust Standards: Medical Advisory Committee
- Patterns of Influenza Vaccination and Vaccine Effectiveness Among Young US Children Who Receive Outpatient Care for Acute Respir
- The Clinical Importance of a Second Dose of Influenza Vaccination in Young Children
- Prevention and Control of Seasonal Influenza with Vaccines
- FluView: Key Updates for Week 17