Ebola Travel Alerts Expanded in Africa

The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reissued high-level Travel Alerts regarding Ebola virus disease outbreaks in various African countries.
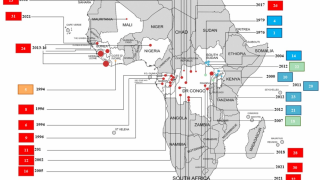
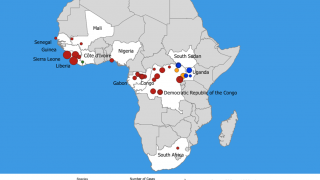
Ebola virus disease (Ebola hemorrhagic fever) is a rare and deadly disease that periodically causes outbreaks in several African countries.
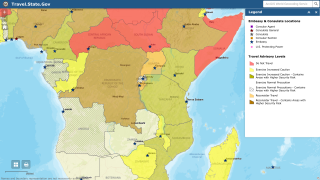
On March 12, 2021, the CDC elevated two Ebola Travel Alerts to Level 3 status, Avoid Nonessential Travel.
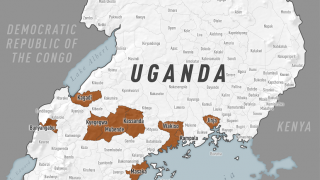
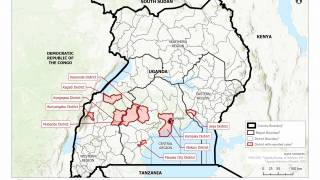
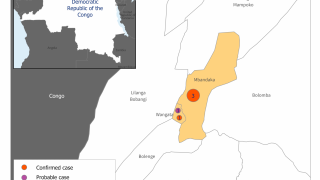
One outbreak is in the North Kivu (Kivu Nord) province in the eastern part of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). A previous episode in this same DRC region began in August 2018 and was declared over in June 2020.
Another Ebola outbreak is ongoing in N’Zérékoré Prefecture of Guinea.
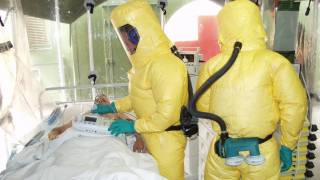
Travelers to these areas could be infected with Ebola if they contact an infected person’s blood or other body fluids. If exposure occurs, people should seek medical care immediately if they develop fever, muscle pain, sore throat, diarrhea, weakness, vomiting, stomach pain, or unexplained bleeding or bruising during or after travel.
Due to the current Ebola outbreaks, the CDC issued an Order on March 4, 2021, requiring airlines to collect and provide the CDC with contact information for passengers in the DRC or Republic of Guinea within 21 days before arriving in the USA.
Public health officials at your U.S. destination may contact you for health monitoring or other public health follow-ups. Learn more about this CDC order at this webpage.
Furthermore, the US Department of State suggests US citizens enroll online in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program to receive security updates and information about getting help in the event of an emergency.
If your job requires possible exposure to Ebola, get vaccinated, says the CDC.
On January 8, 2021, the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommended pre-exposure prophylaxis vaccination with rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP (Ervebo™) for adults ≥ 18 years of age at highest risk for potential occupational exposure to Ebola virus species Zaire ebolavirus.
Merck's Ervebo vaccine's active ingredient is live Vesicular Stomatitis Virus, in which its surface protein has been replaced with that of Zaire ebola virus disease. Inactive ingredients include recombinant human serum albumin, tromethamine buffer. This vaccine contains a trace amount of rice protein.
Although the risk for Ebola is low for most travelers to Guinea, exposure to other diseases, including yellow fever, malaria, polio, hepatitis, rabies, meningitis, and measles, remains high. Before you leave for Guinea, see a travel medicine provider, advises the CDC.
A listing of travel vaccines is published on this Vax-Before-Travel page.
Vax-Before-Travel publishes research-based news.
Our Trust Standards: Medical Advisory Committee