Mpox Vaccinations Effective by Any Route
A recent Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report published by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) confirmed the route of administration of the first dose of Bavarian Nordic JYNNEOS® (MVA-BN) vaccine was not associated with lower overall 2-dose series completion rates during the mpox outbreak in the U.S.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration authorized the JYNNEOS vaccine in August 2022 as a 2-dose series used to prevent mpox virus infection, to be administered via a dose-sparing intradermal (ID) route. The FDA later added authorization for the subcutaneous (SC) route.
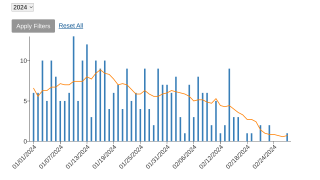
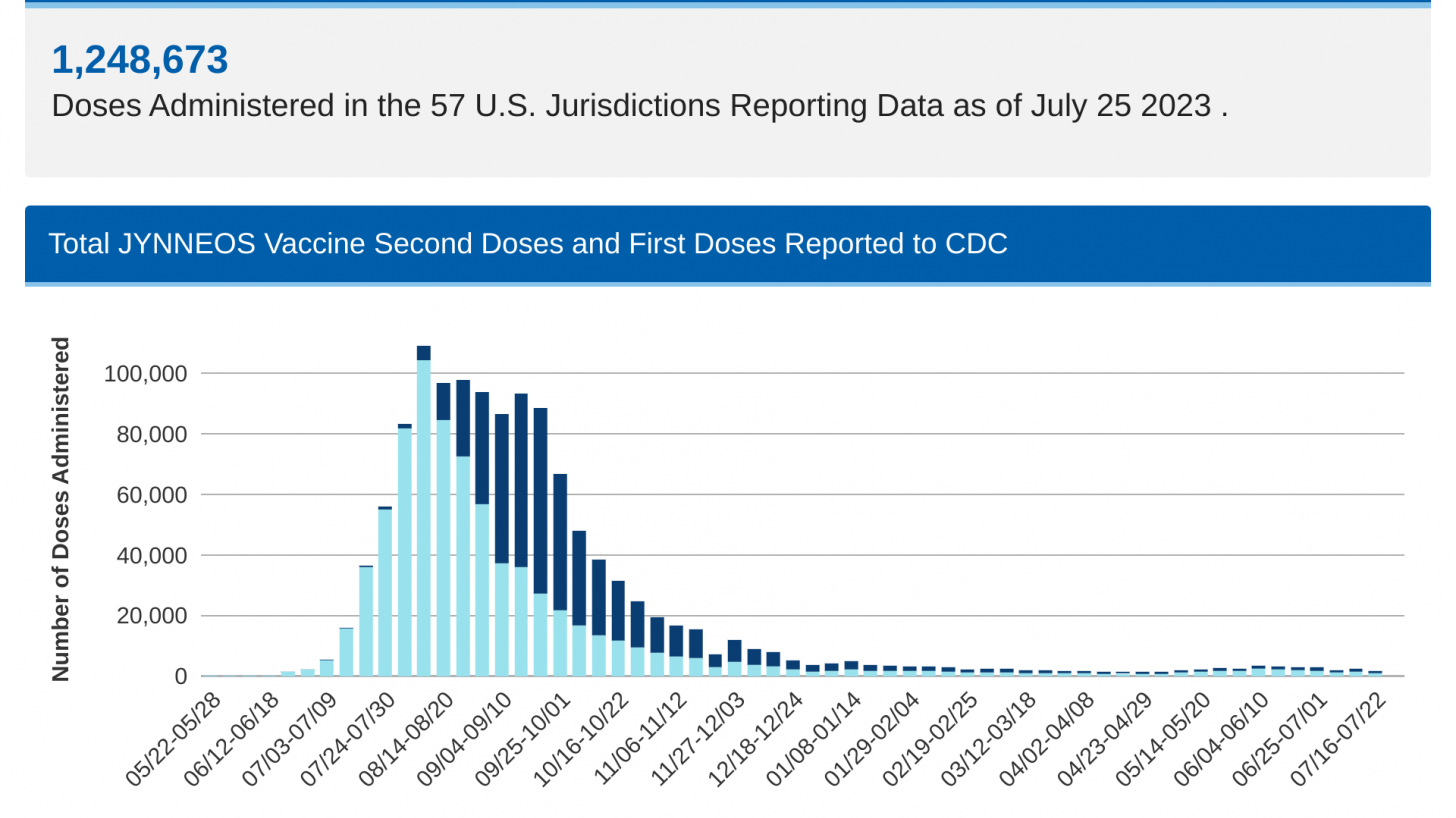
As of July 25, 2023, over 1,248,000 first and second-dose mpox vaccinations had been reported to the CDC.
And in California, 119,345 first doses were administered since August 9, 2022, with the ID route administered by 70% and 30% by the SC route.
To better understand how to administer the JYNNEOS vaccines, the California Department of Public Health investigated whether demographic disparities in vaccination series completion varied by route of administration of the recipient’s first dose.
When the first dose was received by subcutaneous administration, overall series completion was 58.8% compared with 60.2% when the first dose was administered intradermally.
Among California residents who received their first dose from August 9, 2022–March 31, 2023, a total of 59.8% received a second dose.
Series completion was highest among non-Hispanic White persons (64.1%), persons aged ≥65 years (72.6%), and adults with male sex assignment at birth (62.1%).
However, the series completion rate was lowest among non-Hispanic Black or African American persons (51.3%), persons aged 18–24 years (42.9%), and adults assigned female sex at birth (42.8%).
Odds of series completion across all race and ethnicity groups, persons aged 18–64 years, community health conditions, and persons assigned to the male sex at birth were no more significant when the first dose was administered subcutaneously compared with intradermally.
Intradermal use of the JYNNEOS vaccine did not lower overall 2-dose series completion rates, said the CDC on July 28, 2023.
Regarding vaccine effectiveness, The Lancet published results from a study on July 17, 2023, concluding that real-world data estimate vaccine effectiveness to be around 85%.
However, immunological correlates of protection are still unknown.
Previously, the CDC issued a report on June 23, 2023, confirming that a cluster of mpox cases was reported in Chicago, Illinois. And the Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment reported on June 12, 2023, three mpox cases were confirmed in vaccinated people.
As of July 31, 2023, the CDC continues encouraging people to complete the 2-dose series but is not endorsing a third JYNNEOS vaccination.
Since the mpox outbreak began in May 2022, there have been 30,637 cases and 45 related deaths in the U.S.
Our Trust Standards: Medical Advisory Committee