Pneumococcal Vaccination Also Reduces Viral Respiratory Infections

According to emerging evidence, pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCVs) not only prevent pneumococcal disease but also have the potential to indirectly reduce viral respiratory tract infections (RTIs) by affecting pneumococcal-viral interactions.
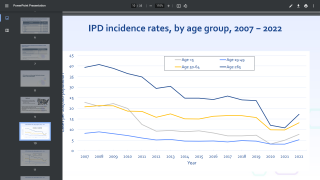
Researchers recently performed a systematic review of interventional and observational studies published between 2000 and 2022 on vaccine efficacy/adjusted effectiveness (VE) and the overall effect of PCV7, PCV9, PCV10, or PCV13 against viral RTI.
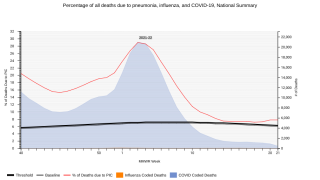
This Major Article, funded by Pfizer Inc., was published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases on March 11, 2024, and concluded the strongest evidence was for influenza in children.
While data from adults were more limited, they were generally consistent with results in children, adding confidence that reported findings represent a true biological effect.
VE against influenza ranged between 41% and 86% (n=4), except for the 2010-2011 influenza season.
In a randomized controlled trial, PCV9 displayed efficacy against viral RTI, human seasonal coronavirus, parainfluenza, and human metapneumovirus. Data in adults were limited (n=3).
PCV13 VE ranged between 4-25% against viral lower RTI, 32-35% against COVID-19 outcomes, 24-51% against human seasonal coronavirus, and 13-36% against influenza A lower RTI, with some 95%CI spanning zero.
This study found PCVs did not offer protection against adenovirus or rhinovirus in children or adults.
These researchers wrote that if the study's results are corroborated, PCV protection against RTIs beyond those due to pneumococci might better capture the full spectrum of PCVs' public health benefits, thereby informing vaccine policymaking and economic evaluations.
As of March 2024, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, the European Medicines Agency, and the U.K.'s NHS have approved various vaccines to prevent pneumococcal disease.
Our Trust Standards: Medical Advisory Committee